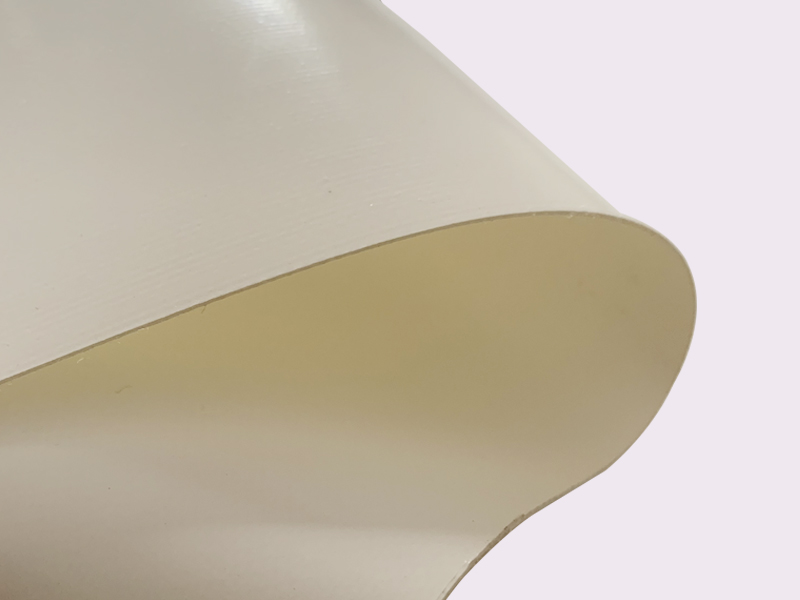
The application of such materials in medical structures and temporary disaster relief structures can greatly reduce diseases and food poisoning caused by environmental exposure and other factors such as common bacteria, and reduce the infection risk of the patients and the wounded. What’s more, it can indirectly reduce the probability of secondary symptoms such as sepsis, and increase the survival rate of internal users in a broad sense.

More Information
| Technical | Technical data | detection basis |
| Base Fabric | 100% polyester | DIN EN 60001 |
| Total Weight(gsm/㎡) | 850gsm/㎡ | DIN EN ISO 2286-2 |
| Total Thickness(mm) | 0.68±0.02mm | |
| Tensile Strength(Warp/Weft)(N/5cm) | 3200/2800N/5cm | DIN 53354 |
| Tear Strength(Warp/Weft)(N) | 400/300N | DIN 53363 |
| Adhesion(N/5cm) | >110N/5cm | DIN 53357 |
| Threshold Temperature | -30℃/+70℃ | DIN EN 1876-2 |
| Surface Treatment | both sides acrylic | |
| Flame Retardancy(can be customized) | B1 | DIN4102 |
| Surface antibacterial properties | Escherichia coli | >99% |
| Staphylococcus aureus | >99% | |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | >99% | |
| Klebsiella pneumonia | >99% | |
| Antibacterial rate | >99% | |
Related Products
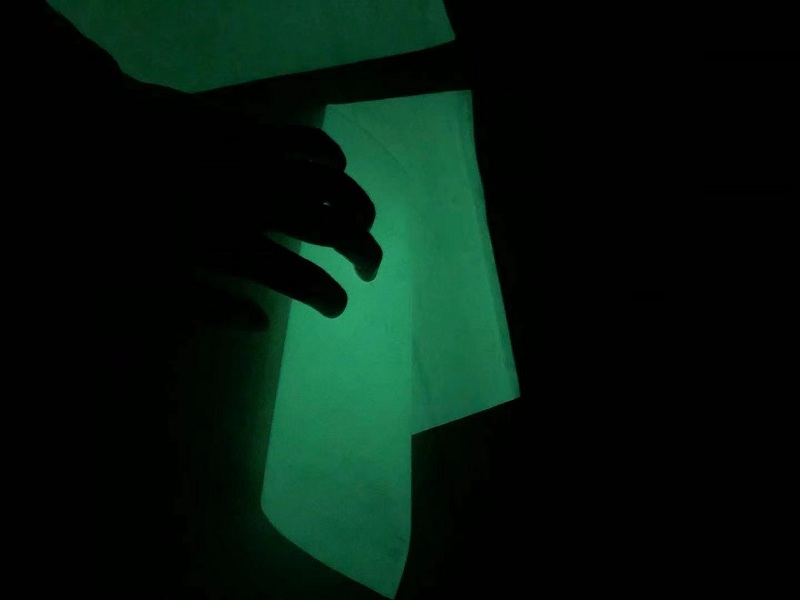

Fluorescent membranes,luminous materials
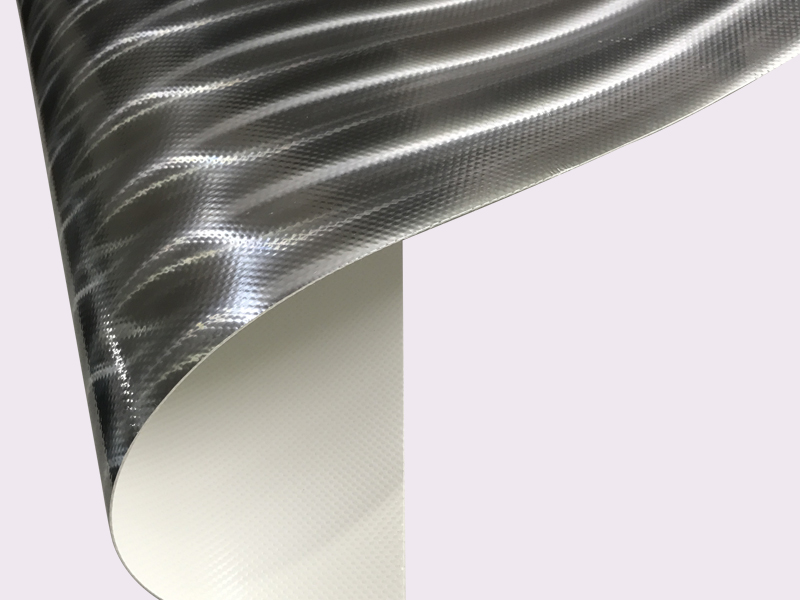
High-quality fabric with high Barrier,anti-corrosion and moisture-proof effect
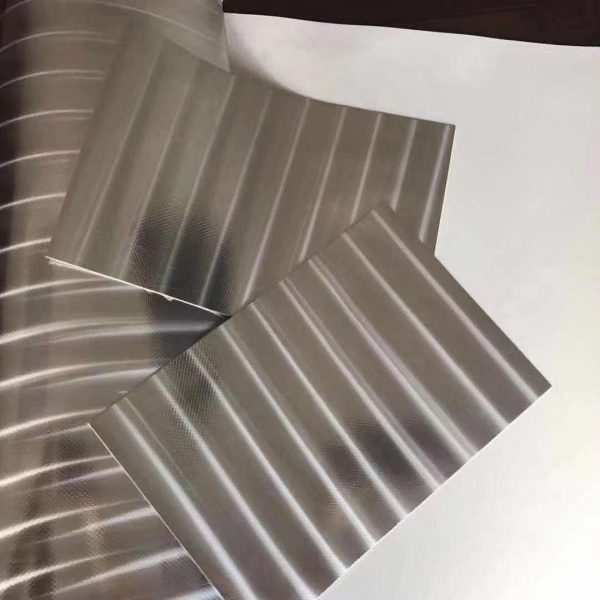

Photovoltaic Reflective Film - PV50

2020 New development products for temporary relief tents
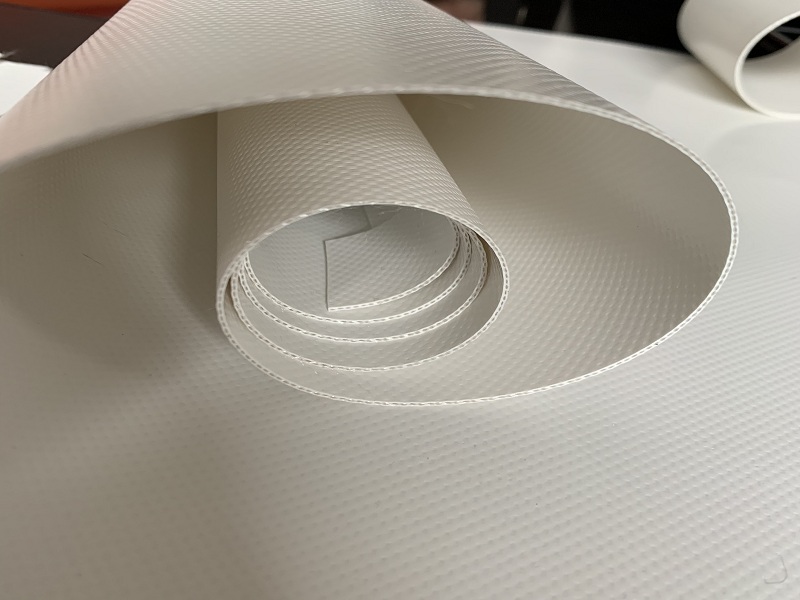
High quality prodect,used for sewage treatment
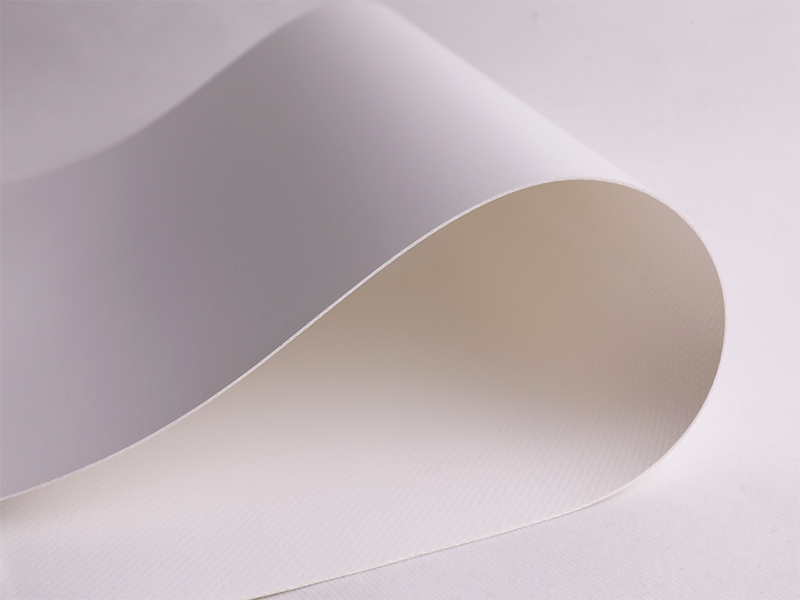
Yellowing and corrosion resistant chemical film
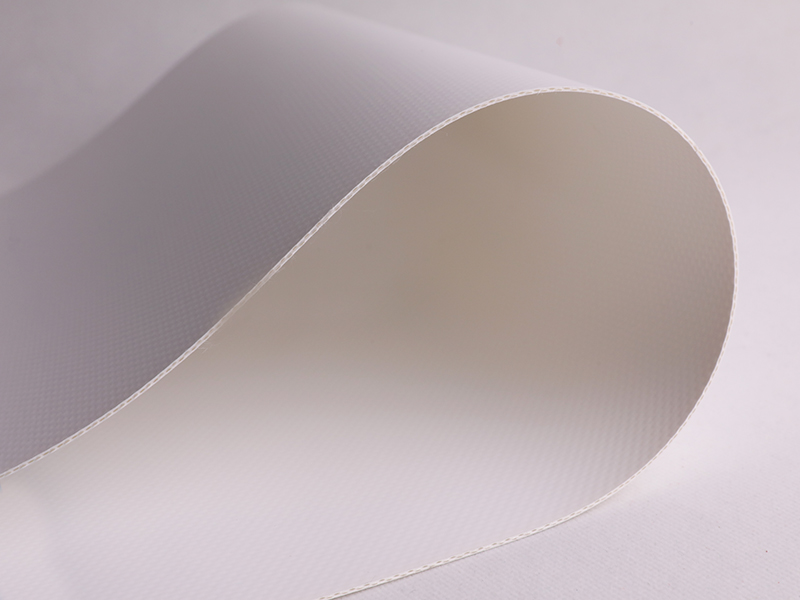

New Air Purifying Film





